Questões de Concurso Comentadas para profissional de nível superior
Foram encontradas 64 questões
Resolva questões gratuitamente!
Junte-se a mais de 4 milhões de concurseiros!
Considere os conjuntos A, B e C no seguinte diagrama:
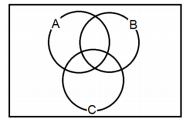
Assinale a alternativa que indica a região
destacada desse diagrama que
representa (B ∩ A) − C.
Um dispositivo de lógica programável tipo FPGA possui uma memória não volátil externa (dataflash) que pode ser gravada por uma interface especial. Essa memória também é conectada aos terminais da FPGA destinados a inicialização (boot) da mesma.
A respeito dessa memória, é correto afirmar que ela desempenha, para a FPGA, o papel fundamental de uma
1. What is an analog-digital converter?
An Analog-Digital Converter (ADC) is a widely used electronic component that converts an analog electric signal (usually a voltage) into a digital representation. The ADCs are at the front-end of any digital circuit that needs to process signals coming from the exterior world. Its schematic symbol is:

The output of a microphone, the voltage at a photodiode or the signal of an accelerometer are examples of analog values that need to be converted so that a microprocessor can work with them.
2. How does the ADC convert a signal?
Many ways have been developed to convert an analog signal, each with its strengths and weaknesses. The choice of the ADC for a given application is usually defined by the requirements you have: if you need speed, use a fast ADC; if you need precision, use an accurate ADC; if you are constrained in space, use a compact ADC.
All ADCs work under the same principle: they need to convert a signal to a certain number of bits N. The sequence of bits represents the number and each bit has the double of the weight of the next, starting from the Most Significant Bit (MSB) up to the Least Significant Bit (LSB). In a nutshell, we want to find the sequence of bits bN−1, bN−2, ..., b0 that represents the analog value Vin as Vin=∑n=0N−1bn2nVref2N.
(www.onmyphd.com/?p=analog.digital.converter. Adaptado)
No trecho da resposta à segunda pergunta – In a nutshell, we want to find the sequence of bits…–, a expressão destacada equivale, em português, a