Questões de Concurso Público BANRISUL 2018 para Desenvolvimento de Sistemas
Foram encontradas 8 questões
Observe as tabelas FUNCIONARIOS, PROJETOS e PARTICIPACOES definidas abaixo, usando SQL, que representam funcionários e a participação destes em projetos.
create table PROJETOS
(codp char(2) not null primary key,
cliente varchar(100) not null,
orcamento numeric(15,2) not null,
pais char(2) not null);
create table FUNCIONARIOS
(matr char(2) not null primary key,
nomef varchar(100) not null,
salario numeric(8,2) not null,
pais char(2) not null);
create table PARTICIPACOES
(codp char(2) not null,
matr char(2) not null,
horas integer not null,
primary key (codp, matr),
foreign key (codp) references PROJETOS,
foreign key (matr) references FUNCIONARIOS);
Observe as instâncias destas tabelas.
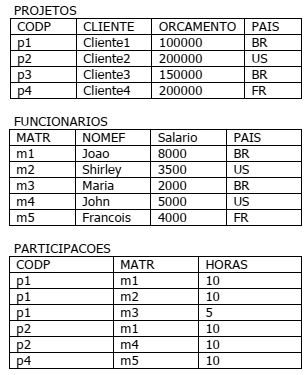
Considere a consulta SQL abaixo, que segue o padrão SQL2.
SELECT cliente
FROM projetos natural left join participacoes natural join funcionarios
GROUP BY codp, cliente
HAVING count(*) > 1;
A consulta SQL acima recuperará
Oberve as tabelas MEDICOS, PACIENTES e CONSULTAS definidas abaixo, usando SQL, que representam médicos, pacientes e as consultas entre estes.
create table ESPECIALIDADES
(code integer not null primary key,
nome varchar(60) not null);
Create table MEDICOS
(codm char(5) not null primary key,
nome varchar(100) not null,
code integer not null,
salario numeric(8,2) not null,
foreign key (code) references ESPECIALIDADES);
Create table CONSULTAS
(codm char(5) not null,
dataHora date not null,
paciente char(5) not null,
primary key (codm, dataHora),
foreign key (codm) references MEDICOS);
Considere as consultas abaixo, formuladas utilizando subconsultas.
 I
I
Quais consultas poderiam ser reescritas usando apenas as cláusulas SELECT-FROM-WHERE, sem usar subconsulta
em nenhuma porção da instrução?
Observe as tabelas FUNCIONARIOS, PROJETOS e PARTICIPACOES definidas abaixo, usando SQL, que representam funcionários e a participação destes em projetos.
Create table PROJETOS
(codp char(2) not null primary key,
cliente varchar(100) not null,
orcamento numeric(15,2) not null,
pais char(2) not null);
create table FUNCIONARIOS
(matr char(2) not null primary key,
nomef varchar(100) not null,
salario numeric(8,2) not null,
pais char(2) not null);
create table PARTICIPACOES
(codp char(2) not null,
matr char(2) not null,
horas integer not null,
primary key (codp, matr),
foreign key (codp) references PROJETOS,
foreign key (matr) references FUNCIONARIOS);
Considere a consulta SQL abaixo.

O que essa consulta SQL recupera?
Observe a tabela PRODUTOS definida em SQL. Considere que existe uma tabela PARTES e que a tabela PRODUTOS possui 50 instâncias.
CREATE TABLE PRODUTOS
(CODP INTEGER NOT NULL,
NOMEP VARCHAR(60) NOT NULL,
PRECO NUMERIC(5,2),
TIPO INTEGER NOT NULL,
PROD_PK PRIMARY KEY(CODP),
FOREIGN KEY (TIPO) REFERENCES PARTES);
Considere que o projetista deseja fazer as seguintes modificações nesta tabela.
I - Remover a chave estrangeira definida sobre o atributo TIPO.
II - Adicionar um novo atributo QT_MIN INTEGER com valor obrigatório (NOT NULL).
III - Remover a chave primária.
IV - Adicionar uma restrição de nome VERIFICA_PRECO, que verifica se o preço é nulo ou maior que 0.
Quais destas alterações podem ser realizadas através de um comando ALTER TABLE aplicado sobre a tabela PRODUTOS?
Observe as tabelas abaixo definidas em SQL.
create table EMPREGADOS
(matr integer not null primary key,
nome varchar(120) not null,
salario numeric(7,2) not null,
funcao varchar(35) not null,
feriasAVencer date);
create table AFASTAMENTOS
(code integer not null primary key,
nome varchar(120) not null,
salario numeric,
funcao varchar(35) not null,
tempo integer);
Considere abaixo a atuação dos comandos SQL de inserção.
I - INSERT INTO AFASTAMENTOS VALUES (1, 'joao', 'gerente');
II - INSERT INTO AFASTAMENTOS (code, nome, tempo, funcao) VALUES (2, 'pedro', 4, 'contador');
III - INSERT INTO AFASTAMENTOS
SELECT matr, nome, salario, funcao
FROM EMPREGADOS
WHERE funcao = 'indefinido';
IV - INSERT INTO AFASTAMENTOS VALUES (3, 'maria',
3000, 'gerente', 1), (4, 'carla', 1500, 'auxiliar', 2).
Quais comandos executam sem falhas?